
What is Coagulation?
Coagulation in wastewater treatment refers to the chemical process where coagulants are added to water to destabilize suspended particles, allowing them to aggregate into larger formations known as flocs. This aggregation facilitates the removal of impurities through subsequent sedimentation and filtration processes. Coagulants neutralize the negative charges on particles, enabling them to come together and form settleable solids.
Types of Coagulants Used
The selection of coagulants is crucial for the efficiency of the coagulation process. Commonly used coagulants include:
Aluminium Sulfate (Alum):
Widely utilized for its effectiveness in removing turbidity and organic matter.
Ferric Chloride and Ferric Sulfate:
Iron-based coagulants known for their proficiency in eliminating heavy metals and phosphates.
Natural Coagulants:
Derived from plant-based sources, these are gaining attention for being environmentally friendly and sustainable alternatives to chemical coagulants.

Removal of Suspended Solids
Coagulation significantly aids in the elimination of suspended solids by promoting their aggregation into larger flocs, which can then be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration. This process enhances water clarity and reduces turbidity, leading to improved overall water quality.
Removal of Additional Contaminants
Beyond suspended solids, coagulation is effective in removing various contaminants, including:
- Heavy Metals: Coagulation precipitates heavy metals, facilitating their removal from wastewater.
- Pathogens: By aggregating and removing particles, coagulation indirectly reduces pathogen levels, contributing to safer water.
These reductions are vital for meeting stringent regulatory standards and safeguarding public health.
Coagulation in Action: Industrial Effluent Treatment Results
Here we see the coagulant at work at one of our clients Industrial Effluent Treatment system:
Before
After


Enhanced Effluent Quality: Application of the coagulant in the industrial effluent treatment plant has led to significant improvements in effluent water quality, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
This example underscores the practical benefits and adaptability of coagulation in diverse wastewater treatment scenarios.
Challenges and Considerations in Coagulation
Several factors influence the efficiency of the coagulation process:
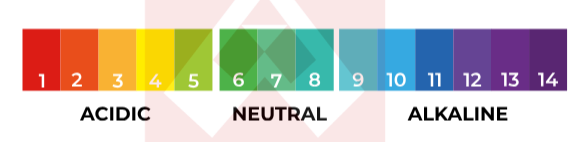
pH Levels:
The effectiveness of coagulants is highly dependent on the pH of the wastewater; optimal pH ranges vary for different coagulants.
Temperature:
Lower temperatures can hinder coagulation efficiency by affecting reaction rates and floc formation.

Coagulant Dosage:
Determining the appropriate amount of coagulant is critical to avoid wastage and ensure effective treatment.
Addressing these challenges requires careful monitoring and adjustment of treatment parameters to optimize coagulation performance.
Conclusion
Coagulation stands as a cornerstone in wastewater treatment, essential for the removal of suspended solids and contaminants, thereby ensuring water quality and regulatory compliance. Understanding its mechanisms, applications, and the factors affecting its efficiency is crucial for industries aiming to implement effective water management practices.
References
Ahmad, T., Ahmad, K., & Alam, M. (2016). Coagulation/flocculation processes and sludge conditioning in wastewater treatment: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 173, 42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.02.007
Choy, S. Y., Prasad, K. M. N., Wu, T. Y., Raghunandan, M. E., & Ramanan, R. N. (2014). Utilization of plant- based natural coagulants as future alternatives towards sustainable water clarification. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 26(11), 2178–2189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.09.012
Genesis Water Technologies. (2021). Coagulants used in water treatment. https://genesiswatertech.com/blog-post/coagulants-used-in-water-treatment/
Malvern Panalytical. (n.d.). What is coagulation in water treatment? Retrieved March 30, 2025, from https://www.malvernpanalytical.com/en/learn/knowledge-center/insights/what-is-coagulation-in- water-treatment

